Traditionally Shakespeare play types are categorised as Comedy, History, and Tragedy, with some additional play categories proposed over the years.
The plays grouped as Shakespeare tragedies follow the Aristotelian model of a noble, flawed protagonist who makes a mistake and suffers a fall from his position, before the normal order is somehow resumed.
List of Shakespeare Tragedy Plays
If you’re interested in learning more about Shakespeare’s tragedies read on, or skip to a section:
Origins of tragedies | Aritsoteloan tragedies | Tragic Shakespeare characters | Death in Shakespeare’s tragedies | Other Shakespeare play types
The Origin of Shakespearean Tragedy
One of the main features of Renaissance art is that it was inspired by classical art and philosophy. This is evident in the work of such artists as Michelangelo who, caught up in the spirit of Humanism that was sweeping across Europe, focused on the human form. Focusing on the human form during Mediaeval times would have been impossible as it would have been a distraction from the necessary focus on God.
The essence of Humanistic art was that human beings were created in God’s image so it was possible for Michelangelo even to portray God – as a beautiful and physically powerful man with realistic human features, presented as perfection – in fact, the human form at its most beautiful. Artists became anatomists, going as far as buying human bodies for dissection. The result was a new realism in the representation of human beings in art.
Shakespeare is, in a way, the Michelangelo of literature. That he could, in one play, Othello, written four hundred years ago, represent what we can recognise as a modern psychopath and a modern alcoholic, in Iago and Cassio respectively, is incredible. Iago is a fully realised psychological character just as David is a fully realized man physically.
Greek drama was an important model for Renaissance drama after the flat, unrealistic morality plays of the medieval centuries. The Greek philosopher, Aristotle, defined tragedy and asserted that it was the noblest and most serious, dignified, and important form of drama. Many of the plays of the Renaissance resembled those Greek tragedies. In several of Shakespeare’s plays, there is a central protagonist who undergoes a harrowing experience as he is brought down from his lofty height, ending up dead.
There is also a special feeling created in an observer of those Shakespeare dramas, similar to the feeling described by Aristotle as the effect of tragedy on an observer. Critics thus thought of those Shakespeare plays as tragedies and that notion has remained with us to this day, although many of those interested in Shakespeare are now thinking differently about the plays from this ‘Shakespearean tragedy’ label. There are still teachers, though, who teach the ‘tragedies’ as though they were Aristotelian tragedies and miss a great deal of what those plays are doing.
An Aristotelian Tragedy
In his Poetics Aristotle outlines tragedy as follows: The protagonist is someone of high estate; a prince or a king. He is like us – perhaps a bit different in his level of nobility so that we can both identify with him and admire him as a man as well as respect him for his high estate. The protagonist has a ‘tragic flaw’ in his character which makes him contribute to his own destruction. This can take the form of an obsession. The flaw is often part of his greatness but it also causes his downfall.
The flaw causes the protagonist to make mistakes and misjudgments that, in turn, begins to alienate him from his supporters so that he becomes isolated. He begins to fall from his high level. He struggles to regain his position but fails and he comes crashing down. He eventually recognises his mistakes, but too late. An important aspect is the suffering he undergoes, which the audience observes and identifies with. We experience ‘pity’ and ‘terror’ as we watch what seems to us an avoidable suffering. At the end, the air is cleared by the restoration of the order that existed before the events of the story and we experience what Aristotle calls ‘catharsis’ – a feeling of relief and closure.
Examples of Shakespeare’s tragic characters
Using the term ‘Shakespean tragedy’ about any of Shakespeare’s plays invites attempts to fit them to the Aristotelian pattern but none of them fits exactly. Othello seems to conform to the pattern but when one thinks about it, Othello, superficially resembling a tragic hero, doesn’t even seem to be the main character in the play. It can be seen as a modern psychological drama about a psychopath who manipulates everyone around him just for fun – just because he has nothing better to do – and destroying other human beings gives him pleasure or is necessary because they get in his way.
Othello may seem to have a fatal flaw – too trusting, gullible – but so do all the other characters, because Iago has deceived them all with his psychopathic charm and a deliberate effort of making himself appear trustworthy. Every misjudgment Othello makes is the hard work of Iago. Easily manipulated? Jealous? Does he have all those ‘tragic flaws’ as well? The feeling at the end is not quite Aristotle either. Perhaps it is more of a disgust for Iago than pity for Othello, who comes across as more stupid than tragic. And to make things more complicated, our feeling of pity is directed more to, Desdemona. And yet some teachers miss the meaning of this play by their insistence on teaching it as an Aristotelian tragedy.
Antony and Cleopatra is sometimes called a ‘double tragedy’. While Othello appears to fit the Aristotelian pattern because of the huge charisma of Othello at the beginning of the play Antony and Cleopatra cannot fit it in any shape or form. In tragedy, the focus is on the mind and inner struggle of the protagonist. The emotional information comes to the audience from that source. In comedy the information comes from a variety of sources and the comic effect is produced by a display of many different points of view, coming at the audience from different angles. That is exactly what happens in Antony and Cleopatra, so we have something very different from a Greek tragedy. What we have is a miracle – a tragic feeling coming out of a comic structure.
So what is Shakespearean tragedy? Perhaps there is no such thing. And yet we can identify tragic moments, feelings and even a cathartic effect in some of the plays. We must be very careful not to insist on fitting them to any pattern because that wouldn’t help us understand the plays. We must look elsewhere for our understanding of them. Moreover, all of Shakespeare’s plays have elements of both tragedy and comedy, sometimes very finely balanced, creating effects that Aristotle could never have dreamt of.
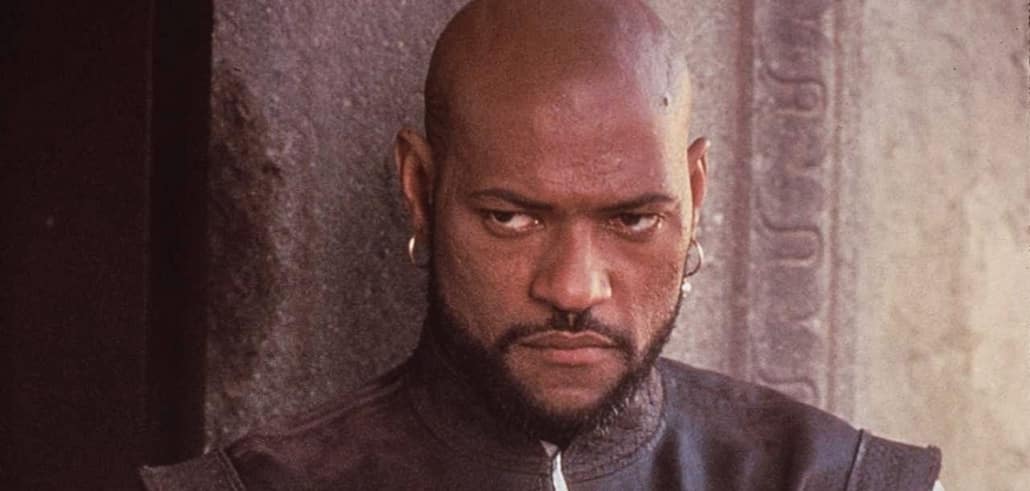

Laurence Fishburn as Othello, classic Shakespearean tragedy protagonist
Death in Shakespeare Tragedies
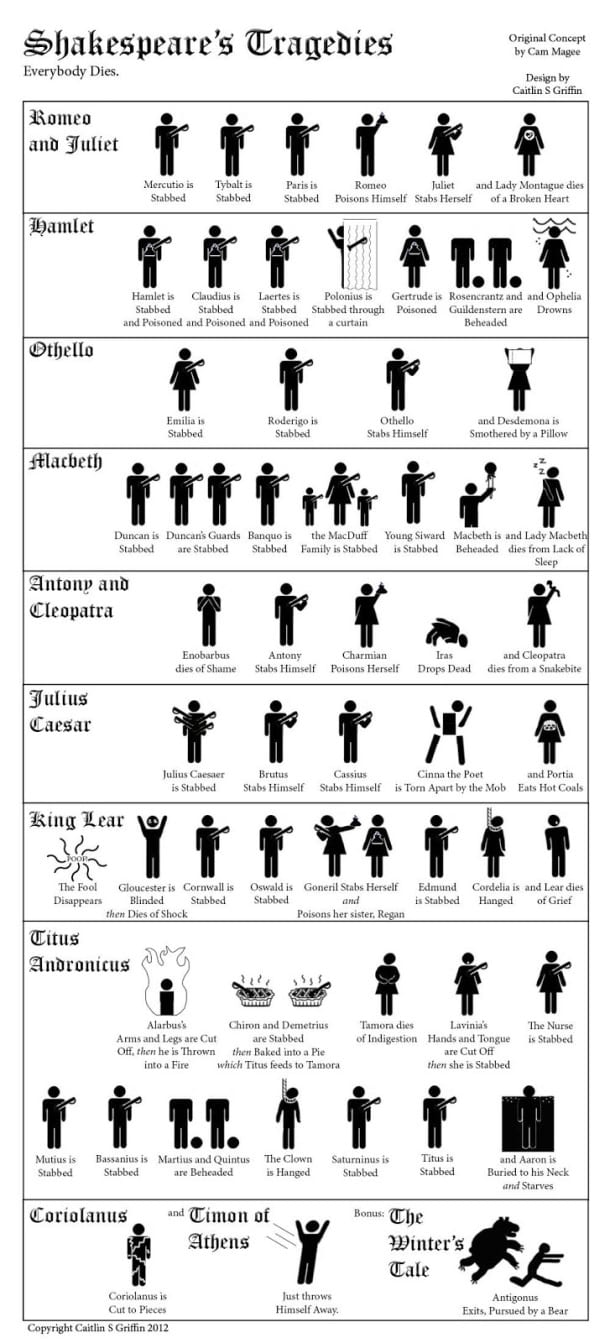
Stabbings, beheadings, poisonings, drownings, snakebites, hanging, cannabalism and more – what a collection of gruesome deaths there were in Shakespeare’s tragedies! This cool infographic from progressivegeographies.com shows how each of Shakespeare’s characters that dies in a Shakespearen tragedy meets their grisly end (and if you’re into death, check out our guide to Shakespeare quotes about death, or read more about the theme of death in Shakespeare’s plays):
,
Like the above? Check out more fun Shakespeare infographics in Pintrest
Other Shakespeare Play Types
Comedy Plays
History Plays
Lost Plays
Masque Plays
Morality Plays
Problem Plays
Roman Plays
Romance Plays
Tragedy Plays
Tragicomedy Plays




i don’t have the info needed
why were you doing this at 2:31 am? and also I dont have the info needed, either
What info were you after Achyu?
this website helped me so much with my project